-
Phone +86 13928238273
-
gigi@polygao.com
Polycarbonate sheets have become increasingly popular in various industries due to their exceptional properties, including high impact resistance, optical clarity, and weather ability.
However, one crucial aspect that significantly influences their performance is their thickness. Here we will talk about how varying thicknesses of polycarbonate sheets can affect their performance in different applications.
Polycarbonate sheets are a type of thermoplastic that exhibits remarkable strength and durability. They are available in various thicknesses, ranging from thin films to thick panels, catering to diverse needs across industries.
Thicker polycarbonate sheets generally offer higher strength and impact resistance compared to thinner sheets.
In applications requiring protection against heavy impacts, such as security glazing and safety barriers, thicker sheets are preferred to ensure optimal performance.
Thin polycarbonate sheets generally offer better optical clarity and light transmission properties compared to thicker sheets.
In applications like greenhouses, skylights, and optical lenses, thinner sheets are favored to allow maximum light penetration while maintaining visual clarity.
Thin polycarbonate sheets tend to be more flexible and easily moldable than thicker sheets. In applications that require bending, shaping, or curving, such as signage and architectural cladding, thinner sheets are the preferred choice.
Thicker polycarbonate sheets have better thermal insulation properties due to their lower thermal conductivity.
For applications like greenhouse roofing or thermal barriers, thicker sheets help maintain a stable interior temperature by reducing heat transfer.
Thin polycarbonate sheets are lighter in weight compared to thicker sheets.
In applications where weight is a crucial factor, such as transportation and aerospace, thinner sheets are used to reduce overall weight while maintaining strength.
Thicker polycarbonate sheets offer better sound insulation properties, making them suitable for applications requiring noise reduction. They are often used in manufacturing acoustic barriers, soundproof windows, and machine enclosures.
Generally, thicker polycarbonate sheets are more expensive than their thinner counterparts.
In budget-sensitive projects, thinner sheets may be preferred, but it's essential to balance cost with the required performance.
Thicker polycarbonate sheets tend to have better fire resistance properties compared to thinner sheets.
In applications where fire safety is critical, such as building facades and transportation interiors, thicker sheets are chosen to meet fire regulations.
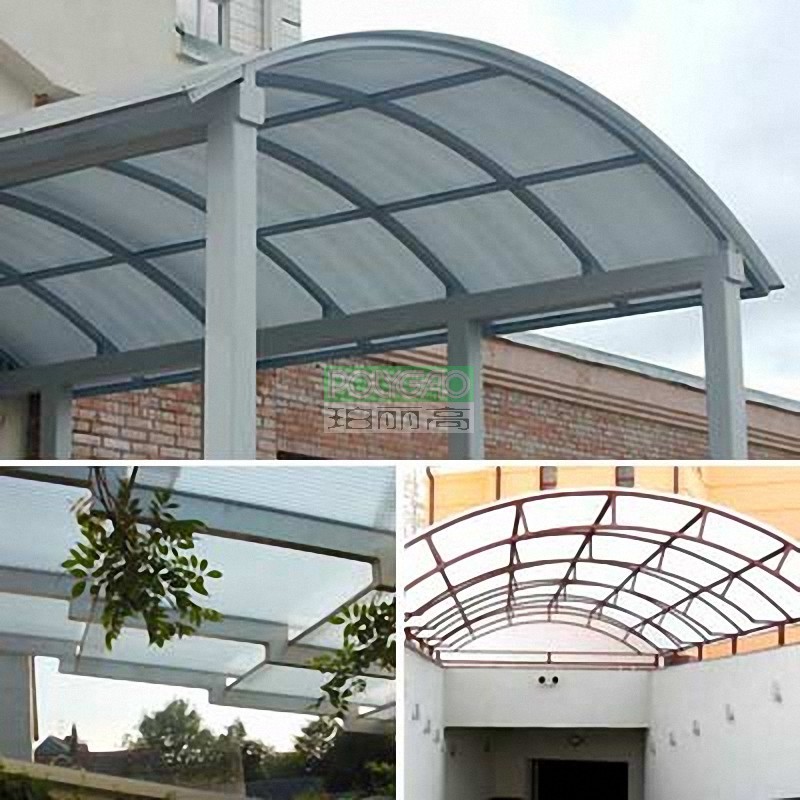

● Greenhouses and Skylights: Thin sheets (1.5mm to 3mm) for optimal light transmission and UV protection.
● Safety Barriers and Security Glazing: Medium-thickness sheets (3mm to 6mm) for enhanced impact resistance.
● Signage and Architectural Cladding: Thin sheets (1mm to 3mm) for ease of formability and lightweight.
● Machine Guards and Soundproofing: Thicker sheets (6mm to 12mm) for improved impact resistance and sound insulation.
● Thermal Barriers and Aerospace: Thicker sheets (6mm to 12mm) for better thermal insulation and strength.
While thin sheets offer excellent optical clarity and flexibility, thicker sheets provide enhanced strength and thermal insulation. Choosing the right thickness of polycarbonate sheet is crucial to ensure optimal performance in various applications.
Understanding the specific requirements of each application will guide you in selecting the most suitable polycarbonate sheet thickness, taking into account factors such as impact resistance, cost, weight, and fire performance. By making an informed choice, you can harness the full potential of polycarbonate sheets to meet the diverse demands of your projects.
Contact Polygao today to explore cost comparisons between thin and thick polycarbonate sheets and find the perfect solution for your project.